请注意,本文编写于 845 天前,最后修改于 845 天前,其中某些信息可能已经过时。
目录
aapt命令在Android测试中的强大实用
一、aapt命令介绍
aapt(Android Asset Packaging Tool)是Android系统提供的一个打包Android应用资源的命令行工具。它可以用来列出、查看和处理apk包中的资源文件。掌握aapt命令可以帮助我们更好地理解Android应用的结构,以及修改已有的apk。
bashAndroid Asset Packaging Tool
Usage:
aapt l[ist] [-v] [-a] file.{zip,jar,apk}
List contents of Zip-compatible archive.
aapt d[ump] [--values] [--include-meta-data] WHAT file.{apk} [asset [asset ...]]
strings Print the contents of the resource table string pool in the APK.
badging Print the label and icon for the app declared in APK.
permissions Print the permissions from the APK.
resources Print the resource table from the APK.
configurations Print the configurations in the APK.
xmltree Print the compiled xmls in the given assets.
xmlstrings Print the strings of the given compiled xml assets.
aapt p[ackage] [-d][-f][-m][-u][-v][-x][-z][-M AndroidManifest.xml] \
[-0 extension [-0 extension ...]] [-g tolerance] [-j jarfile] \
[--debug-mode] [--min-sdk-version VAL] [--target-sdk-version VAL] \
[--app-version VAL] [--app-version-name TEXT] [--custom-package VAL] \
[--rename-manifest-package PACKAGE] \
[--rename-instrumentation-target-package PACKAGE] \
[--utf16] [--auto-add-overlay] \
[--max-res-version VAL] \
[-I base-package [-I base-package ...]] \
[-A asset-source-dir] [-G class-list-file] [-P public-definitions-file] \
[-D main-dex-class-list-file] \
[-S resource-sources [-S resource-sources ...]] \
[-F apk-file] [-J R-file-dir] \
[--product product1,product2,...] \
[-c CONFIGS] [--preferred-density DENSITY] \
[--split CONFIGS [--split CONFIGS]] \
[--feature-of package [--feature-after package]] \
[raw-files-dir [raw-files-dir] ...] \
[--output-text-symbols DIR]
Package the android resources. It will read assets and resources that are
supplied with the -M -A -S or raw-files-dir arguments. The -J -P -F and -R
options control which files are output.
aapt r[emove] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 ...]
Delete specified files from Zip-compatible archive.
aapt a[dd] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 ...]
Add specified files to Zip-compatible archive.
aapt c[runch] [-v] -S resource-sources ... -C output-folder ...
Do PNG preprocessing on one or several resource folders
and store the results in the output folder.
aapt s[ingleCrunch] [-v] -i input-file -o outputfile
Do PNG preprocessing on a single file.
aapt v[ersion]
Print program version.
Modifiers:
-a print Android-specific data (resources, manifest) when listing
-c specify which configurations to include. The default is all
configurations. The value of the parameter should be a comma
separated list of configuration values. Locales should be specified
as either a language or language-region pair. Some examples:
en
port,en
port,land,en_US
-d one or more device assets to include, separated by commas
-f force overwrite of existing files
-g specify a pixel tolerance to force images to grayscale, default 0
-j specify a jar or zip file containing classes to include
-k junk path of file(s) added
-m make package directories under location specified by -J
-u update existing packages (add new, replace older, remove deleted files)
-v verbose output
-x create extending (non-application) resource IDs
-z require localization of resource attributes marked with
localization="suggested"
-A additional directory in which to find raw asset files
-G A file to output proguard options into.
-D A file to output proguard options for the main dex into.
-F specify the apk file to output
-I add an existing package to base include set
-J specify where to output R.java resource constant definitions
-M specify full path to AndroidManifest.xml to include in zip
-P specify where to output public resource definitions
-S directory in which to find resources. Multiple directories will be scanned
and the first match found (left to right) will take precedence.
-0 specifies an additional extension for which such files will not
be stored compressed in the .apk. An empty string means to not
compress any files at all.
--debug-mode
inserts android:debuggable="true" in to the application node of the
manifest, making the application debuggable even on production devices.
--include-meta-data
when used with "dump badging" also includes meta-data tags.
--pseudo-localize
generate resources for pseudo-locales (en-XA and ar-XB).
--min-sdk-version
inserts android:minSdkVersion in to manifest. If the version is 7 or
higher, the default encoding for resources will be in UTF-8.
--target-sdk-version
inserts android:targetSdkVersion in to manifest.
--max-res-version
ignores versioned resource directories above the given value.
--values
when used with "dump resources" also includes resource values.
--version-code
inserts android:versionCode in to manifest.
--version-name
inserts android:versionName in to manifest.
--replace-version
If --version-code and/or --version-name are specified, these
values will replace any value already in the manifest. By
default, nothing is changed if the manifest already defines
these attributes.
--custom-package
generates R.java into a different package.
--extra-packages
generate R.java for libraries. Separate libraries with ':'.
--generate-dependencies
generate dependency files in the same directories for R.java and resource package
--auto-add-overlay
Automatically add resources that are only in overlays.
--preferred-density
Specifies a preference for a particular density. Resources that do not
match this density and have variants that are a closer match are removed.
--split
Builds a separate split APK for the configurations listed. This can
be loaded alongside the base APK at runtime.
--feature-of
Builds a split APK that is a feature of the apk specified here. Resources
in the base APK can be referenced from the the feature APK.
--feature-after
An app can have multiple Feature Split APKs which must be totally ordered.
If --feature-of is specified, this flag specifies which Feature Split APK
comes before this one. The first Feature Split APK should not define
anything here.
--rename-manifest-package
Rewrite the manifest so that its package name is the package name
given here. Relative class names (for example .Foo) will be
changed to absolute names with the old package so that the code
does not need to change.
--rename-instrumentation-target-package
Rewrite the manifest so that all of its instrumentation
components target the given package. Useful when used in
conjunction with --rename-manifest-package to fix tests against
a package that has been renamed.
--product
Specifies which variant to choose for strings that have
product variants
--utf16
changes default encoding for resources to UTF-16. Only useful when API
level is set to 7 or higher where the default encoding is UTF-8.
--non-constant-id
Make the resources ID non constant. This is required to make an R java class
that does not contain the final value but is used to make reusable compiled
libraries that need to access resources.
--shared-lib
Make a shared library resource package that can be loaded by an application
at runtime to access the libraries resources. Implies --non-constant-id.
--app-as-shared-lib
Make an app resource package that also can be loaded as shared library at runtime.
Implies --non-constant-id.
--error-on-failed-insert
Forces aapt to return an error if it fails to insert values into the manifest
with --debug-mode, --min-sdk-version, --target-sdk-version --version-code
and --version-name.
Insertion typically fails if the manifest already defines the attribute.
--error-on-missing-config-entry
Forces aapt to return an error if it fails to find an entry for a configuration.
--output-text-symbols
Generates a text file containing the resource symbols of the R class in the
specified folder.
--ignore-assets
Assets to be ignored. Default pattern is:
!.svn:!.git:!.ds_store:!*.scc:.*:<dir>_*:!CVS:!thumbs.db:!picasa.ini:!*~
--skip-symbols-without-default-localization
Prevents symbols from being generated for strings that do not have a default
localization
--no-version-vectors
Do not automatically generate versioned copies of vector XML resources.
--no-version-transitions
Do not automatically generate versioned copies of transition XML resources.
--private-symbols
Java package name to use when generating R.java for private resources.
常用命令
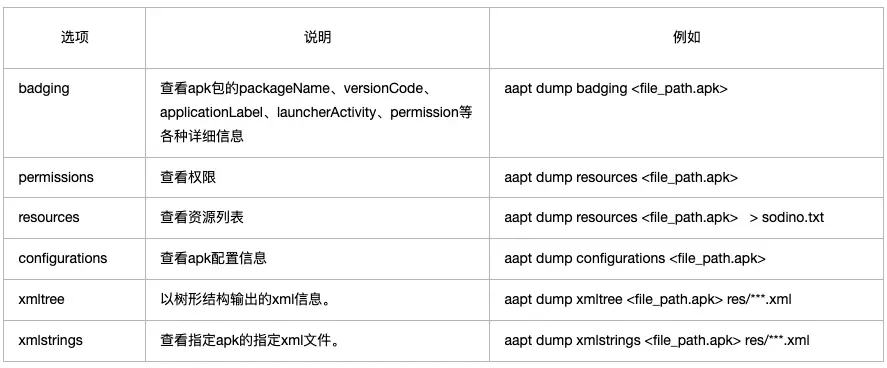
二、aapt命令功能
- 列出apk包的内容
使用
aapt list APK_FILE可以列出apk包里的内容,比如Activity、Service等组件、权限等信息。 命令:
aapt list demo.apk
执行上述命令后,会列出apk的详细信息,包括:
通过
aapt list命令可以清楚地了解apk包的组成内容和结构,这对逆向分析apk非常有帮助。
csskotlin/KotlinVersion.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/PreconditionsKt.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmField.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/Strictfp.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmStatic.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmPackageName.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmSuppressWildcards.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmName.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmOverloads.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmWildcard.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmMultifileClass.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/Volatile.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/Synchronized.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/Transient.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmInline.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmSynthetic.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/jvm/JvmRecord.kotlin_metadata
kotlin/UnsignedUtilsKt.kotlin_metadata
firebase-common.properties
network-common.properties
HMSCore-ui.properties
HMSCore-base.properties
network-grs.properties
META-INF/ymtchannel_FR_MKT_ZYOPPO
META-INF/Uchannel_应用市场
打印的内容
- 支持的屏幕尺寸 - 语言配置 - 动画资源 - 菜单资源 - 布局资源 - drawables资源 - values资源 - 样式资源 - 颜色状态列表资源 - 字体资源 - 纹理资源 - xml资源 - 权限 - instrumentation类名 - uses-permission元素 - uses-features元素 - main activity - 其他activities - services - receivers - providers - 包名 - 版本号 - sdk版本
- 查看apk一些信息
使用
aapt dump badging APK_FILE可以显示apk的版本信息、支持的屏幕、权限等。 命令:
aapt dump badging demo.apk
aapt dump badging提供的信息对快速了解apk的配置非常有帮助。
package: name='com.tianmao.app' versionCode='91680' versionName='V3.40.265' compileSdkVersion='28' compileSdkVersionCodename='9' sdkVersion:'19' targetSdkVersion:'27' uses-library-not-required:'org.apache.http.legacy' other-activities other-receivers other-services supports-screens: 'small' 'normal' 'large' 'xlarge' supports-any-density: 'true' locales: '--_--' 'zh' densities: '120' '160' '240' '320' '480' '640' '65534' native-code: 'arm64-v8a'
执行命令后,会显示apk的详细信息,包括:
- 包名 - 版本号 - sdk版本 - 目标sdk版本 - uses-permission权限 - application标签信息 - launchable activity - screen支持的屏幕尺寸 - native-code指明是否使用了native code - supports-screens显示支持的屏幕信息 - locales显示支持的地区 - densities显示支持的屏幕密度
三、aapt命令实战应用
- 查看apk中的Activity 命令:
aapt dump xmltree APK_FILE AndroidManifest.xml
这将解析AndroidManifest.xml文件,并显示所有的标签信息,可以清楚看到apk中声明的所有Activity。
- 修改apk中的图标 首先用aapt命令解压apk包:
aapt unpack APK_FILE tmp/
这会将apk文件的内容解压到tmp目录下。然后可以修改tmp/res/drawable中的图标文件ic_launcher.png。
修改完成后,使用aapt重新打包:
aapt package -F NEW_APK_FILE -M AndroidManifest.xml -S res/ -I android.jar
这样就可以修改好apk包中的图标。
- 修改apk的版本信息 同样先解压apk,然后编辑tmp/AndroidManifest.xml文件,修改versionCode、versionName等版本信息。 最后使用aapt重新打包即可。
- 移除不需要的资源文件 可以使用aapt remove移除多余资源:
aapt remove APK_FILE res/drawable-xhdpi/*
这样可以删除drawable-xhdpi中的图片资源,起到精简apk的作用。
四、aapt命令总结
aapt命令在Android开发和逆向分析中非常实用,掌握它可以大大提高研究和修改apk包的效率。
aapt的主要用途包括:
- 查看apk的详细信息
- 编译编辑Android资源文件
- 直接操作已打包好的apk 在实际应用中,aapt命令可以辅助开发,也是逆向分析必备工具。全面掌握aapt的用法,可以帮助我们更好地理解和开发Android应用。
如果对你有用的话,可以打赏哦
打赏


本文作者:李佳玮
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录